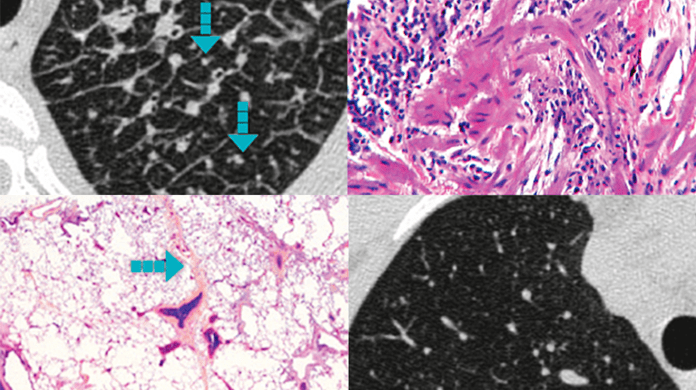
Cum să suspectăm fibroza pulmonară?
- o amenințare comună într-o gamă largă de pneumopatii interstițiale difuze (PID), inclusiv pneumopatii interstițiale difuze asociate bolilor de țesut conjunctiv (PID-BTC). Fibroza pulmonară poate deveni un factor cheie al afectării ireversibile și al mortalității precoce și necesită identificarea și intervenția urgentă.1–4

DESCOPERIȚI ADEVĂRATUL IMPACT AL PID CU FENOTIP FIBROZANT PROGRESIV
Diagnosticul PID
Pentru pacienții aflați la risc, HRCT ar trebui să fie efectuat la prima suspiciune de PID cu fenotip progresiv.1,5–8
Monitorizarea precoce și regulată
Timpul este esențial atunci când PID FFP este suspectată.9
Amenințarea critică a PID-FFP
Fibroza pulmonară este un pericol pentru mai multe tipuri de PID.1–4

Evaluarea inițială a PID
Identificarea precoce a fibrozei pulmonare poate îmbunătăți povara bolii.9–12
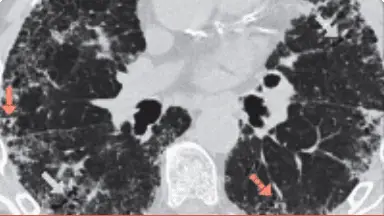
Imagistica HRCT în fibroza pulmonară
Tomografia computerizată de înaltă rezoluție este esențială pentru diagnosticarea precisă a PID.13

Intervențiile din cadrul PID
Tratamentul precoce este esențial în FPI și ar putea să influențeaze pozitiv progresia.14-18

Modelul SPIKES: cum să să comunici vești negative pacienților
Profesorul Walter Baile ne prezintă prin Modelul SPIKES modul de structurare al conversațiilor dificile.
Exacerbările acute ale PID
Un pericol care ar putea lovi oricând.17–21

Cazuri de pacienți cu PID pentru evaluare și diagnostic
Descărcați cazurile pacienților noștri: istoricul medical al pacienţilor reprezentativi.
- Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Wells AU, et al. Design of the PF-ILD trial: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial of nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease. BMJ Open Resp Res. 2017;4(1):e000212.
- Patterson KC, Strek ME. Pulmonary fibrosis in sarcoidosis. Clinical features and outcomes. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10(4):362-370.
- Caban JJ, Yao J, Bagci U, Mollura DJ. Monitoring pulmonary fibrosis by fusing clinical, physiological, and computed tomography features. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011;6216-6219.
- Wells AU, Brown KK, Flaherty KR, Kolb M, Thannickal VJ, on behalf of the IPF Consensus Working Group. Eur Resp J. 2018;51:1800692.
- Theodore AC, Tseng C-H, Li N, Elashoff RM, Tashkin DP. Correlation of cough with disease activity and treatment with cyclophosphamide in scleroderma interstitial lung disease: findings from the Scleroderma Lung Study. Chest. 2012;142(3):614–621.
- Hoffmann-Vold AM, Fretheim H, Halse AK, et al. Tracking impact of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis in a complete nationwide cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200:1258–1266.
- Hoffmann-Vold AM, Maher TM, Philpot EE, et al. The identification and management of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: evidence-based European consensus statements. The Lancet Rheumatology. 2020b;2:e71–e83.
- Asano Y, Jinnin M, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Diagnostic criteria, severity classification and guidelines of systemic sclerosis: Guideline of SSc. J Dermatol. 2018;45, 633–691.
- Cottin V, Hirani N, Hotchkin D, et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(150):180076.
- Chaudhuri N, Spencer L, Greaves M, et al. A Review of the Multidisciplinary Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective Analysis in a Single UK Specialist Centre. J Clin Med. 2016;5(66):1–9.
- Cottin V, Brown KK. Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc–ILD). Respir Res. 2019a;20(1):13.
- Wong AW, Ryerson C, Guler S. Progression of fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir Res. 2020:29;21(1):32.
- Brauner M, et al. Imagerie des pneumopathies infiltrantes diffuses. Press Med. 2010;39:73–84.
- Maher TM, Molina-Molina M, Russell AM, et al. Unmet needs in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-insights from patient chart review in five European countries. BMC Pulm Med. 2017;17(1):124.
- Molina-Molina M, Aburto M, Acosta O, et al. Importance of early diagnosis and treatment in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Rev Resp Med. 2018;12(7):537–539.
- Robalo-Cordeiro C, Campos P, Carvalho L, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the era of antifibrotic therapy: Searching for new opportunities grounded in evidence. Rev Port Pneumol. 2017;23(5):287–293.
- Kolb M, Bondue B, Pesci A, et al. Acute exacerbations of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(150):pii:180071.
- Song JW, Hong S-B, Lim C-M, et al. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: incidence, risk factors and outcome. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(2):356–363.
- Song JW, Lee HK, Lee CK, et al. Clinical course and outcome of rheumatoid arthritis-related usual interstitial pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2013;30(2):103-112.
- Tomiyama F, Watanabe R, Ishii T, et al. High Prevalence of Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease in Japanese Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2016;239, 297–305.
- Okamoto M, Fujimoto K, Sadohara J, et al. A retrospective cohort study of outcome in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Respiratory Investigation. 2016;54, 445–453.