Fiziopatologia comună a PID-BTC
În timp ce PID sunt diferite, căile patogenice către fibrogeneză sunt comune independent de factorul declanșator al leziunii pulmonare1-4
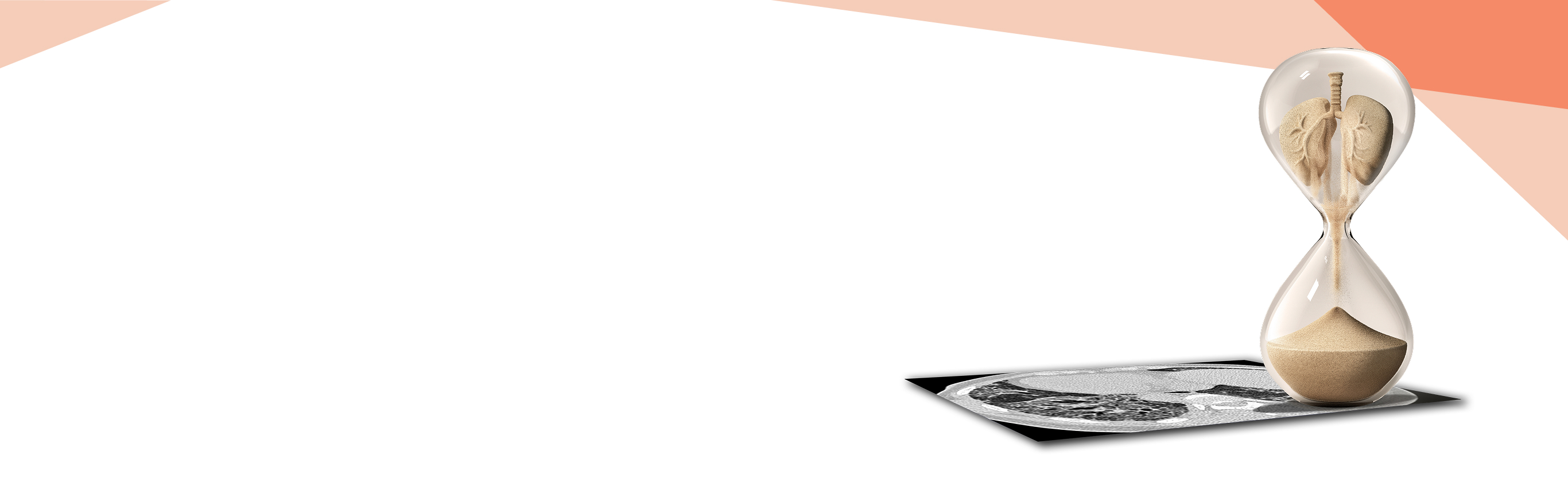

PATOGENEZA PID-BTC IMPLICĂ INTERACȚIUNEA PRECOCE ÎN EVOLUȚIA BOLII DINTRE INFLAMAȚIE ȘI FIBROZĂ5-7
MECANISMELE PATOGENICE COMUNE ALE FIBROZEI PULMONARE ÎN PID-BTC
Aflați despre mecanismele fiziopatologice aplicabile unei game largi de PID-BTC fibrotice care pot dezvolta un fenotip fibrozant progresiv
În timp ce PID diferă, căile patogene comune către fibrogeneză sunt comune1,2,4,8,9
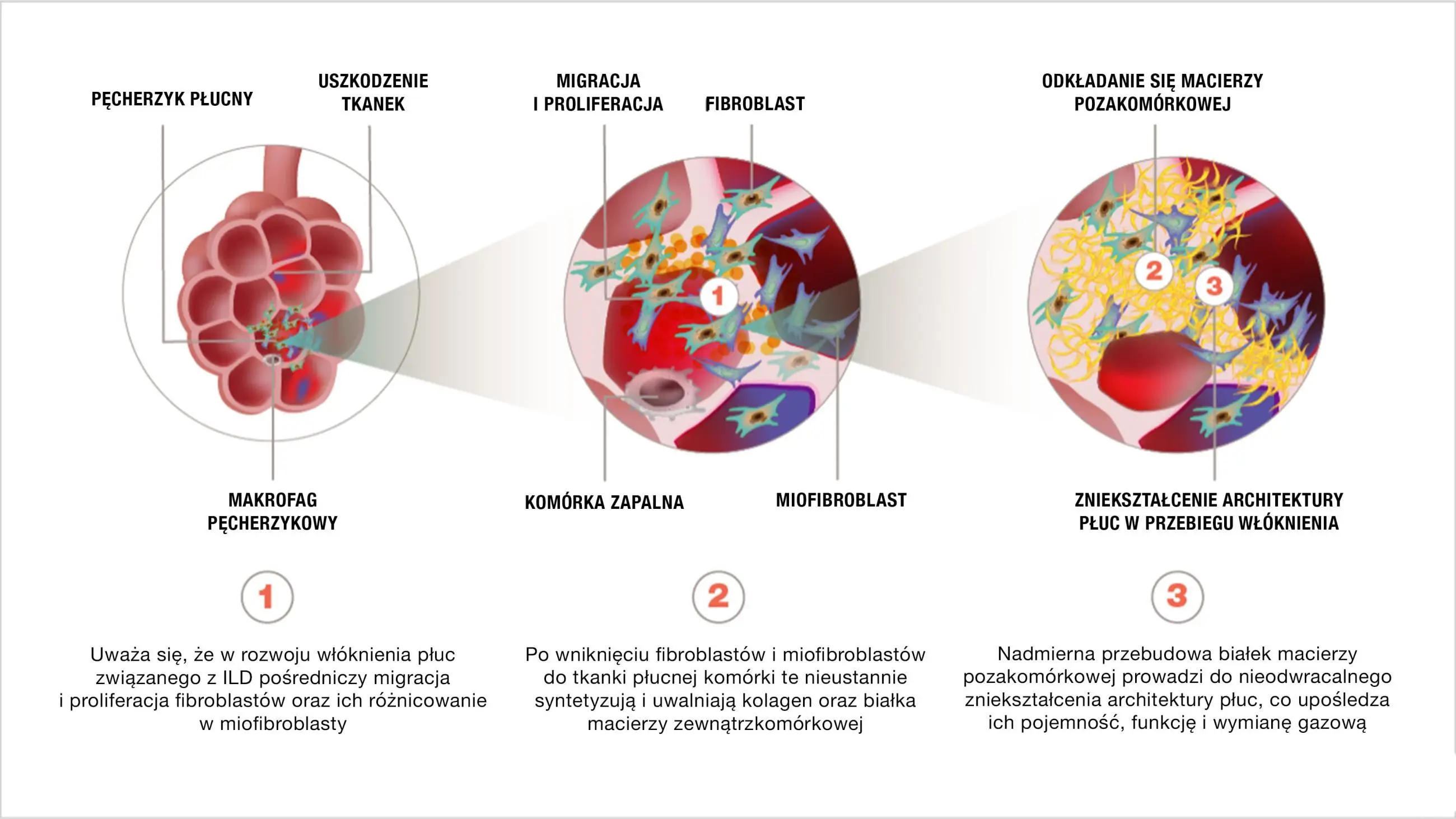
O interacțiune complexă a proceselor inflamatorii, fibrotice și vasculare duce la activarea și proliferarea fibroblastelor, diferențierea lor în miofibroblaste și secreția excesivă a matricei extracelulare5,6,10
Aflați mai multe despre interacțiunea dintre inflamație și fibroză în PID-BTC
PID-BTC POT ÎMPĂRTĂȘI MECANISME DE AUTO-ÎNTREȚINERE ALE FIBROZEI PULMONARE PROGRESIVE4,10
Indiferent de diagnosticul clinic, există aspecte comune în mecanismul patogen care stau la baza care conduce un proces auto-întreținut de fibroză pulmonară4
Odată ce fibroza pulmonară devine un proces auto-întreținut, fibroblastele pot deveni parțial independente de stimularea externă și de răspunsul inflamator inițial11,12
Progresia auto-întreținută a fibrozei5,13,14
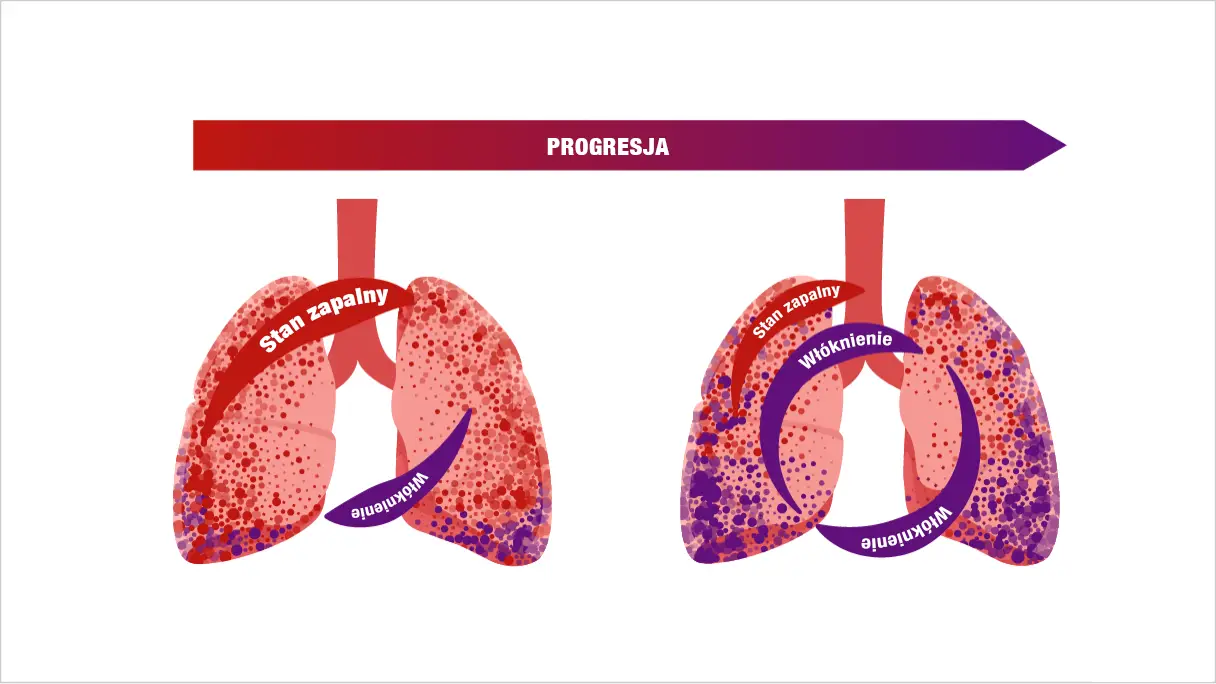
Aflați mai multe despre fibroza progresivă auto-întreținută în PID-BTC
Cum puteți depista și diagnostica PID fibrozantă la debut în cazul pacienților dumneavoastră cu BTC?
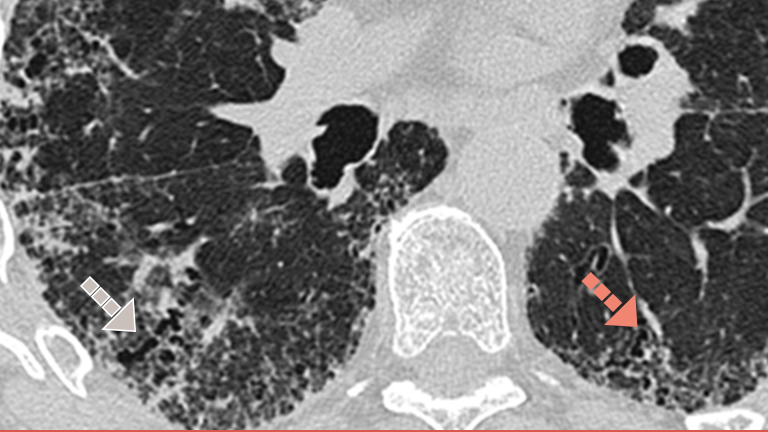
Investigarea PID-BTC fibrozante cu imagistica HRCT

Screening pentru PID în BTC
Diagnosticul PID-BTC
Note
-
BTC, boala țesutului conjunctiv; PID-BTC, pneumopatie interstițială difuză asociată cu boli ale țesutului conjunctiv; HRCT, tomografie computerizată de înaltă rezoluție; PID, pneumopatie interstițială difuză
- Cottin V, Hirani N, Hotchkin D, et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(150):180076.
- Wuyts WA, Agostini C, Antoniou KM, et al. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis: a moving target. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(5):1207–1218.
- Maher TM, Wuyts W. Management of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Adv Ther. 2019;36(7):1518–1531.
- Kolb M, Vašáková M. The natural history of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Respir Res. 2019;20(1).
- Wells AU, Denton CP. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disease— mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10:728–739.
- Castelino FV and Varga J. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue diseases: evolving concepts of pathogenesis and management. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):213. doi: 10.1186/ar3097.
- Dellaripa PF. Interstitial lung disease in the connective tissue diseases; a paradigm shift in diagnosis and treatment. Clin Immunol. 2018;186:71–73.
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134(2):136–151.
- Bagnato G and Harari S. Cellular interactions in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24(135):102–114.
- Fischer A and Distler J. Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease associated with systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(10):2673–2681.
- Distler J, et al. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2019(b):15:705–30.
- Kolb M, Flaherty KR. The justification for the progressive fibrotic phenotype. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2021; online ahead of print.
- Saketkoo LA, Scholand MB, Lammi MR, et al. Patient-reported outcome measures in systemic sclerosis–related interstitial lung disease for clinical practice and clinical trials. Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2020;5(2 Suppl): 48–60.
- Wollin L, Distler JHW, Redente EF, et al. Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 2019;54(3):1900161. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00161-2019.
- Brauner M, et al. Imagerie des pneumopathies infiltrantes diffuses. Press Med. 2010;39:73–84.
- Geerts S, Wuyts W, De Langhe E, et al. Connective tissue disease associated interstitial pneumonia: a challenge for both rheumatologists and pulmonologists. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2017;34(4):326–335.
- Wallace B, Vummidi D, Khanna D. Management of connective tissue diseases associated interstitial lung disease: a review of the published literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(3):236–245.
