Fiziopatologia comună a PID-BTC
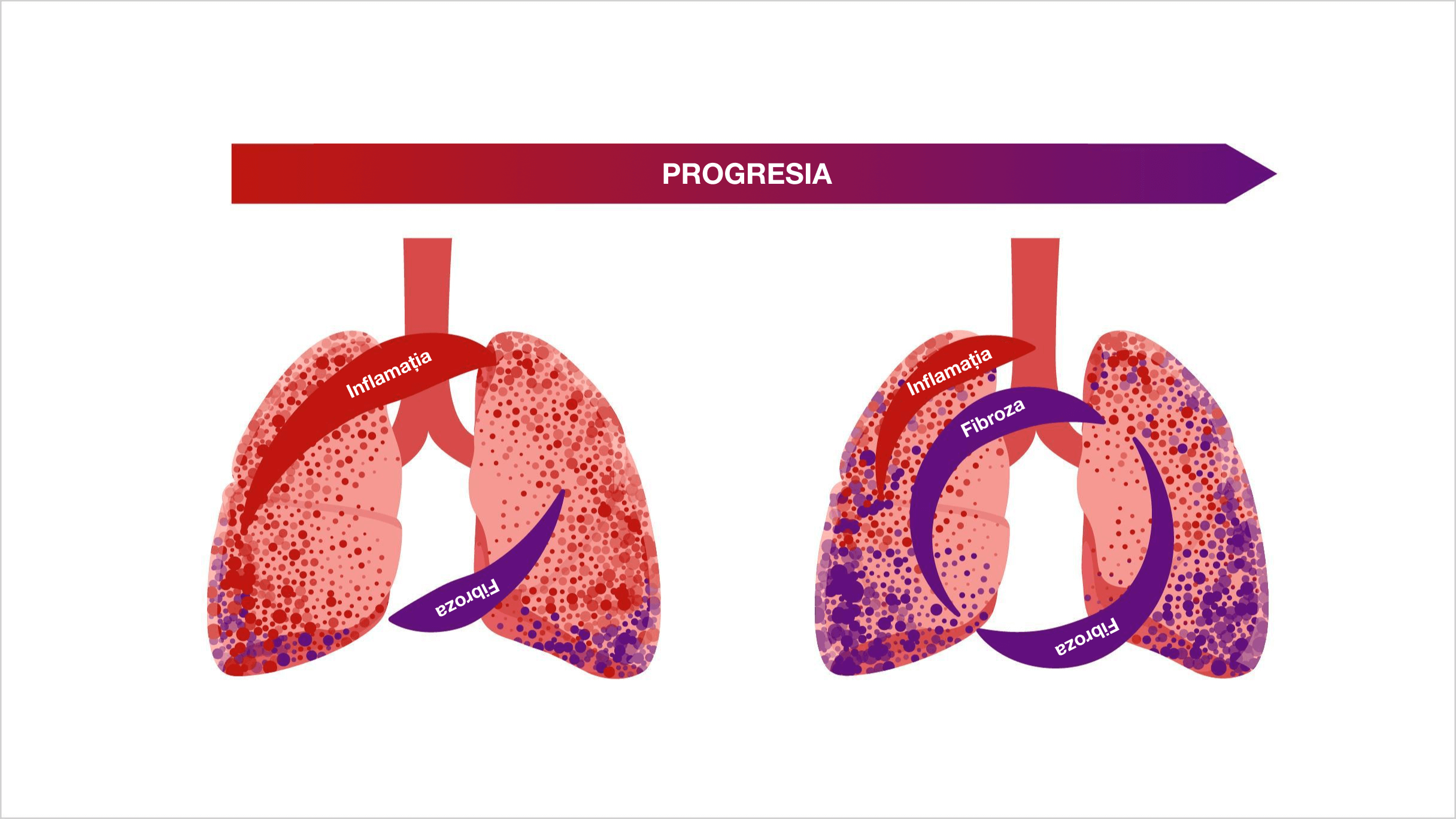
În timp ce PID sunt diferite, căile patogenice către fibrogeneză sunt comune independent de factorul declanșator al injuriei pulmonare1–4

PATOGENEZA PID-BTC IMPLICĂ INTERACȚIUNEA PRECOCE ÎN EVOLUȚIA BOLII DINTRE INFLAMAȚIE ȘI FIBROZĂ5-7
MECANISMELE PATOGENICE COMUNE ALE FIBROZEI PULMONARE ÎN PID-BTC
Aflați despre mecanismele fiziopatologice aplicabile unei game largi de PID-BTC fibrotice care pot dezvolta un fenotip fibrozant progresiv
În timp ce PID diferă, căile patogene comune către fibrogeneză sunt comune1,2,4,8,9
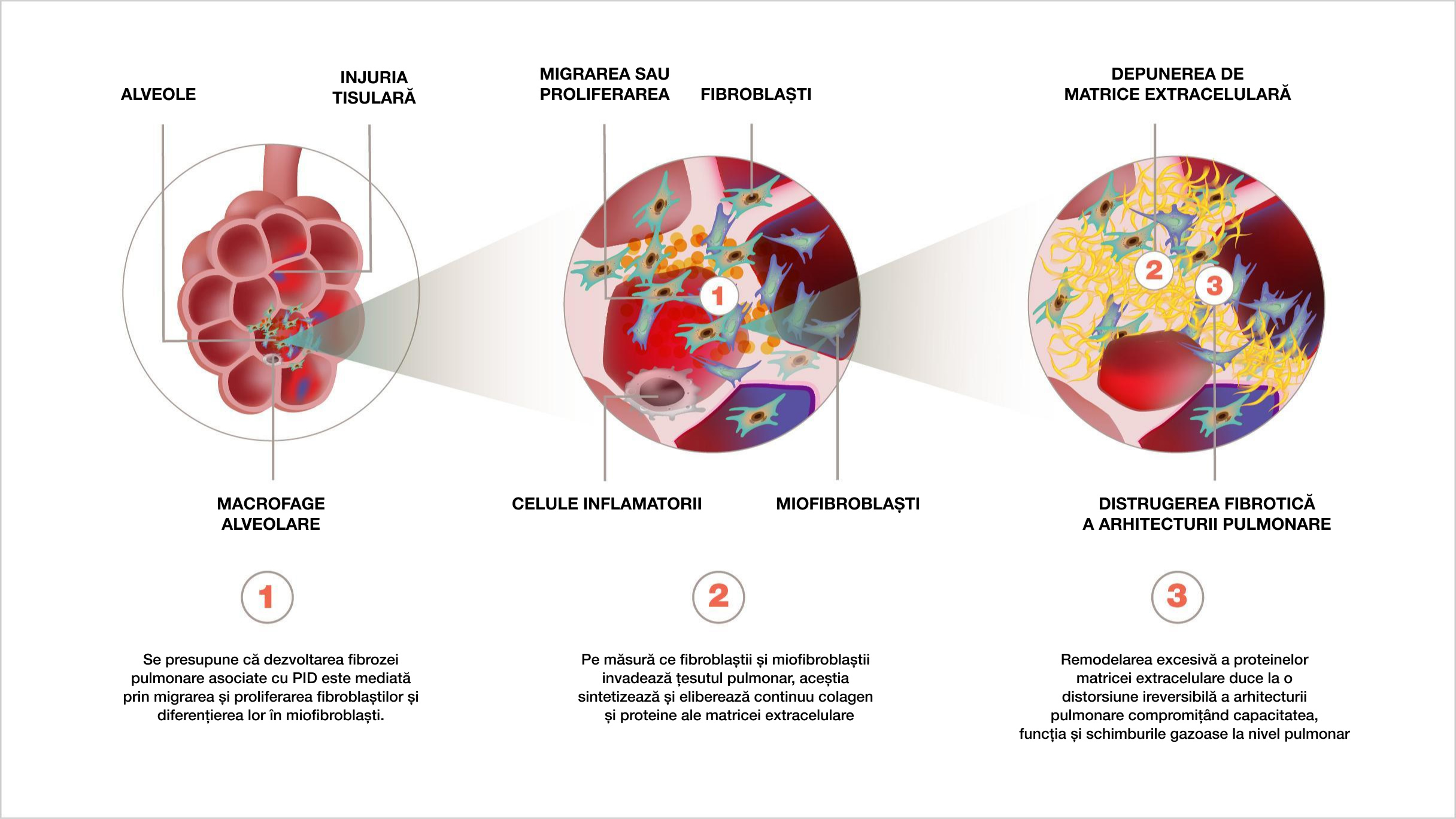
O interacțiune complexă a proceselor inflamatorii, fibrotice și vasculare duce la activarea și proliferarea fibroblastelor, diferențierea lor în miofibroblaste și secretia excesiva a matricei extracelulare5,6,10
Aflați mai multe despre interacțiunea dintre inflamație și fibroză în PID-BTC
PID-BTC POT ÎMPĂRTĂȘI MECANISME DE AUTO-ÎNTREȚINERE ALE FIBROZEI PULMONARE PROGRESIVE4,10
Indiferent de diagnosticul clinic, există aspecte comune în mecanismul patogen care stau la baza care conduce un proces auto-întreținut de fibroză pulmonară4
Odată ce fibroza pulmonară devine un proces auto-întreținut, fibroblastele pot deveni parțial independente de stimularea externă și de răspunsul inflamator inițial11,12
Progresia auto-întreținută a fibrozei5,13,14
Cum puteți depista și diagnostica PID fibrozantă la debut în cazul pacienților dumneavoastră cu BTC?
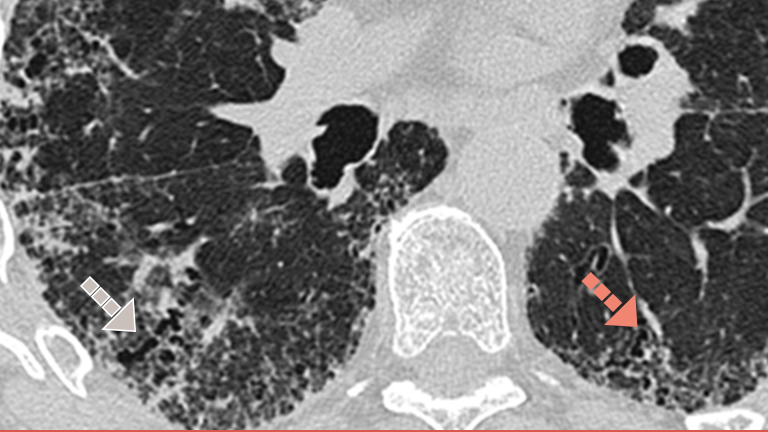
Cum puteți depista și diagnostica PID fibrozantă la debut în cazul pacienților dumneavoastră cu BTC?

Screening pentru PID în BTC
Diagnosticul PID-BTC
Note
-
BTC, boala țesutului conjunctiv; PID-BTC, pneumopatie interstițială difuză asociată cu boli ale țesutului conjunctiv; HRCT, tomografie computerizată de înaltă rezoluție; PID, pneumopatie interstițială difuză
-
- Cottin V, Hirani N, Hotchkin D, et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(150):180076.
- Wuyts WA, Agostini C, Antoniou KM, et al. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis: a moving target. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(5):1207–1218.
- Maher TM, Wuyts W. Management of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Adv Ther. 2019;36(7):1518–1531.
- Kolb M, Vašáková M. The natural history of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Respir Res. 2019;20(1).
- Wells AU, Denton CP. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disease— mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10:728–739.
- Castelino FV and Varga J. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue diseases: evolving concepts of pathogenesis and management. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):213. doi: 10.1186/ar3097.
- Dellaripa PF. Interstitial lung disease in the connective tissue diseases; a paradigm shift in diagnosis and treatment. Clin Immunol. 2018;186:71–73.
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134(2):136–151.
- Bagnato G and Harari S. Cellular interactions in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24(135):102–114.
- Fischer A and Distler J. Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease associated with systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(10):2673–2681.
- Distler J, et al. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2019(b):15:705–30.
- Kolb M, Flaherty KR. The justification for the progressive fibrotic phenotype. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2021; online ahead of print.
- Saketkoo LA, Scholand MB, Lammi MR, et al. Patient-reported outcome measures in systemic sclerosis–related interstitial lung disease for clinical practice and clinical trials. Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2020;5(2 Suppl): 48–60.
- Wollin L, Distler JHW, Redente EF, et al. Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 2019;54(3):1900161. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00161-2019.
- Brauner M, et al. Imagerie des pneumopathies infiltrantes diffuses. Press Med. 2010;39:73–84.
- Geerts S, Wuyts W, De Langhe E, et al. Connective tissue disease associated interstitial pneumonia: a challenge for both rheumatologists and pulmonologists. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2017;34(4):326–335.
- Wallace B, Vummidi D, Khanna D. Management of connective tissue diseases associated interstitial lung disease: a review of the published literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(3):236–245.